Live Home 3D Workspace
The Program Settings
To display the program settings, click the menu button and select Settings.
The General, 2D and 3D sections contain the application settings. The Project section lets you set up the current project. It is described separately.
General
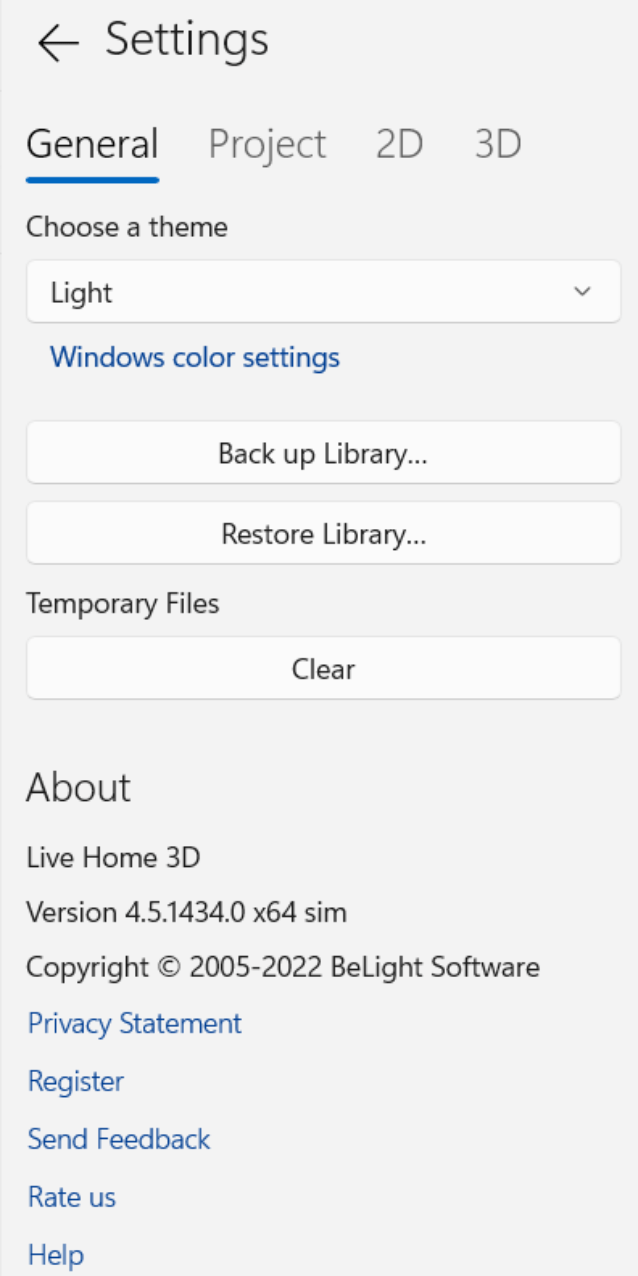
The Choose a theme drop-down menu lets you select a color theme. Choose Default to have the same theme as the operating system has.
The Windows color settings button opens the color settings of the operating system.
The Back up Library… button backs up the material and object libraries.
The Restore Library… button restores the material and object libraries.
The Clear button removes unnecessary temporary files and thumbnails of library objects when there is no any open or unsaved document.
2D

1 – Activate or deactivate snapping. This option concerns the behavior of drawing tools and objects when you move or resize them. When enabled, objects will snap to one another when in close proximity.
2 – Snap Sensitivity defines how close the selected object needs to be to another before the objects snap together.
3 – Show or hide the grid. The program sets up the grid spacings automatically depending on the zoom percentage of the 2D view.
4 – Show or hide rulers.
5 – Show or hide floor labels that can display the floor area and some other information.
6 – Activate or deactivate smart guidelines and snapping to them. These guidelines show up temporarily when you move a tool or object near another object in order to help you align them correctly.
7 – Show or hide walls of the story above the current one.
8 – Show or hide walls of the story below the current one.
9 – Show or hide the Site layer.
10 – Show or hide the compass.
11 – Show or hide the viewpoint. When it is on, the viewpoint is usually displayed as a blue triangle on the floor plan.
12 – Show or hide the ceiling light fixtures. You may need to hide lamps if they block the view to other objects.
13 – Make locked objects semi-transparent on the floor plan.
14 – Show or hide furniture in the elevation view.
3D
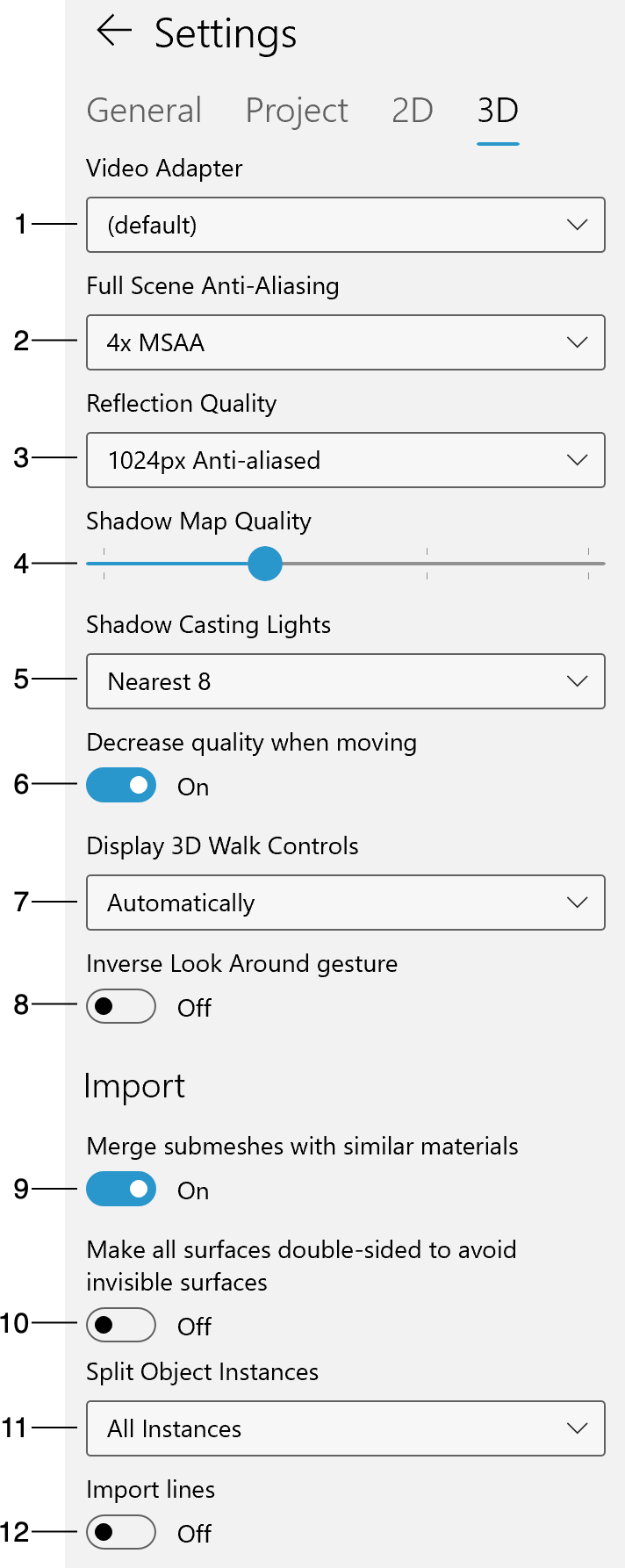
1 – Video Adapter
2 – Full Scene Anti-Aliasing
3 – Reflection Quality
4 - Shadow Map Quality
5 – Shadow Casting Lights
6 – Decrease quality when moving
7 – Display 3D Walk Controls
8 – Inverse Look Around Gesture
9 – Merging Submeshes
10 – Make Surfaces Double-sided
11 – Split Object Instances
12 – Import Lines
1 – Select your video adapter type. There are usually two or three options in the list. Your computer can have one or two video adapters. The list also includes the "Microsoft Basic Render Driver" item which provides software rendering. It is slower than a hardware accelerated video adapter, so use this option only if the others don't work. In the case of two video adapters, one, as a rule, provides better performance while another consumes less energy. For comfortable work, choose the more powerful one.
2 – Full Scene Anti-Aliasing makes the picture look softer by smoothing the edges of objects. When this option is off, diagonal lines may look jugged.

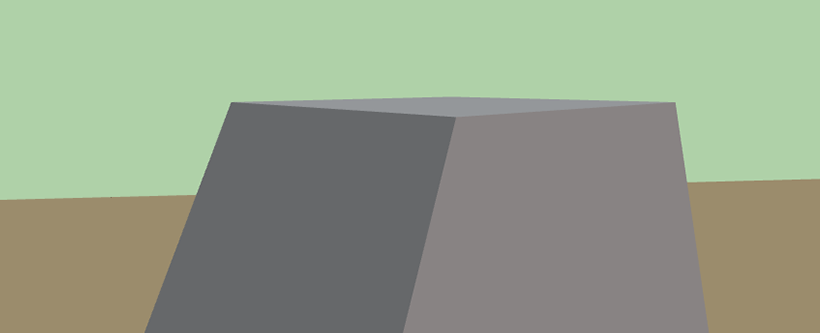
3 – The Reflection Quality defines the quality of the reflections displayed in objects such as mirrors. This parameter affects the resolution of the reflections and also the strength of anti-aliasing. At lower quality, the picture may look more pixelated, but rendering will be faster.
4 – The Shadow Map Quality lets you adjust the rendering quality in the Shadow Maps mode. At low quality, shadows can look blurred.
5 – Shadow Casting Lights defines how many light sources (including the sun and moon) are taken into account when the program is rendering shadows. At smaller numbers, rendering is faster.
Note that if the quantity of considered light sources is too small, you can get an unrealistic picture because you cannot see shadows that normally exist.
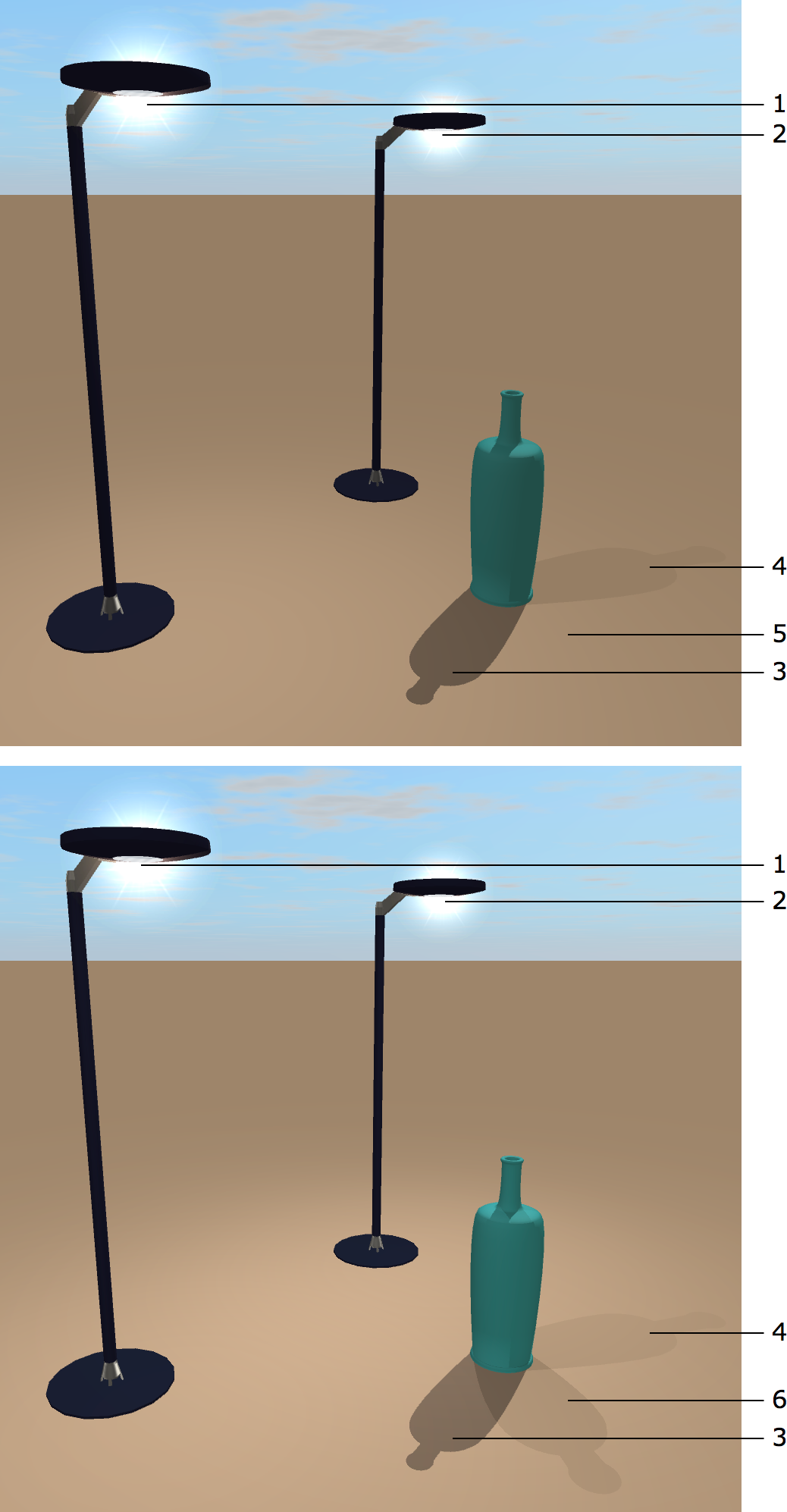
1 – Light source 1
2 – Light source 2
3 – Shadow from the sun
4 – Shadow from the light source 1
5 – No shadow from the light source 2 with Shadow Casting Lights set to Nearest 2
6 – Shadow from the light source 2 with Shadow Casting Lights set to Nearest 4
Limiting the number of objects that cast shadow can also increase the program performance.
6 – The Decrease quality when moving option can change the rendering mode automatically. When this option is activated, the program turns off reflections, shadows and lights while you are walking around in 3D. When you stay still, lights, reflections and shadows restore. Note that if lights and shadows are already turned off in the toolbar, then nothing will change when you start walking in 3D.
7 – Display 3D Walk Controls. The joystick is more useful if you prefer touchscreen gestures. The central Walk Control is easier to use with the mouse. For more details, read Walk Controls.
8 – Inverse Look Around Gesture lets you invert the direction of rotation for the Look Around tool.
9 – Merging submeshes, if activated, takes place when you import an object. By merging submeshes, the program can remove excessive details from the object model. More details can be found in the Import Options section.
10 – This option fixes objects with surfaces created inside out. Without repair, such defective objects appear as having holes or missing parts in the 3D view. Only those objects are affected that were imported when this option is on. Not all objects can be fixed this way. More details can be found in the Import Options section.
11 – The Split Object Instances option separates parts of an object you import. As a result you get an object that can be ungrouped in the 2D view. Not all objects can be split this way. More details can be found in the Import Options section.
12 – When the Import lines option is deactivated, the program ignores lines. Such lines can be created using the Line tool in the SketchUp or other software.
Note that the settings located at the end of the Full Scene Anti-Aliasing, Reflection Quality and Shadow Casting Lights drop-down lists offer better rendering quality but require higher device performance.